
 0086 0755 21380136
0086 0755 21380136
 0086 0755 21380136
0086 0755 21380136
 sales@megarevo.com.cn
sales@megarevo.com.cn
 2024-12-06
2024-12-06
 Industry information
Industry information
 Megarevo
Megarevo
Inverters are a crucial component in the conversion of direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), and thus play a pivotal role in PV power systems, wind power systems and other fields. This paper will examine the technical specifications, advantages, and challenges associated with off-grid inverters, on-grid inverters, and hybrid inverters.
Inverter Type
Off-Grid Inverter
Off-grid inverters are typically used in solar power systems that are not connected to the grid. Their function is to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to supply power to homes or small independent power grids, without being directly connected to the public power grid.
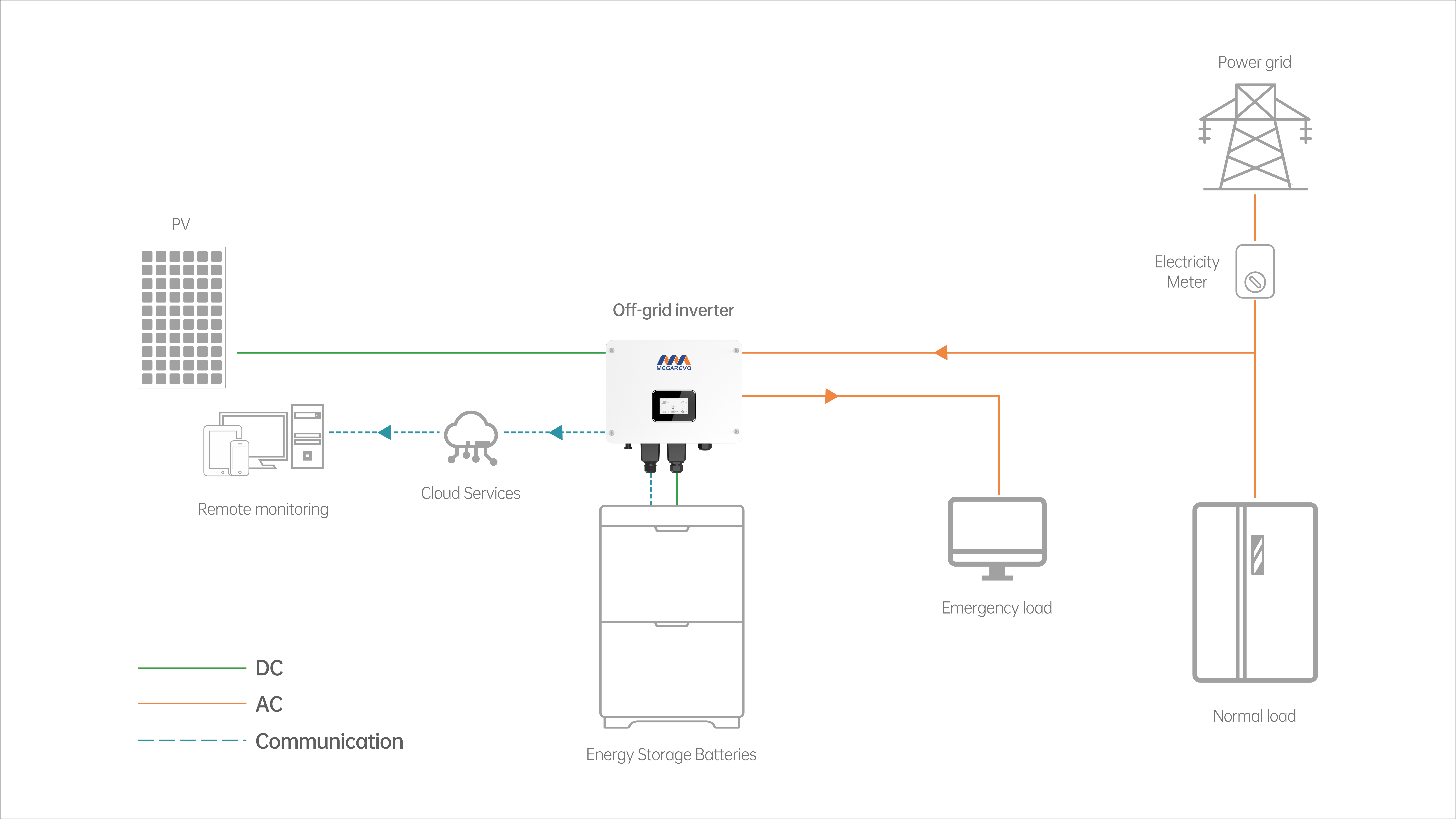
On-grid Inverter
On-grid inverters are primarily used in PV power generation systems to convert the direct current (DC) generated by distributed clean energy into alternating current (AC) that is synchronized with the power grid, achieving the interconnection and complementarity of multiple energy sources. They are mainly used to integrate distributed power sources into large-scale electrical grids."
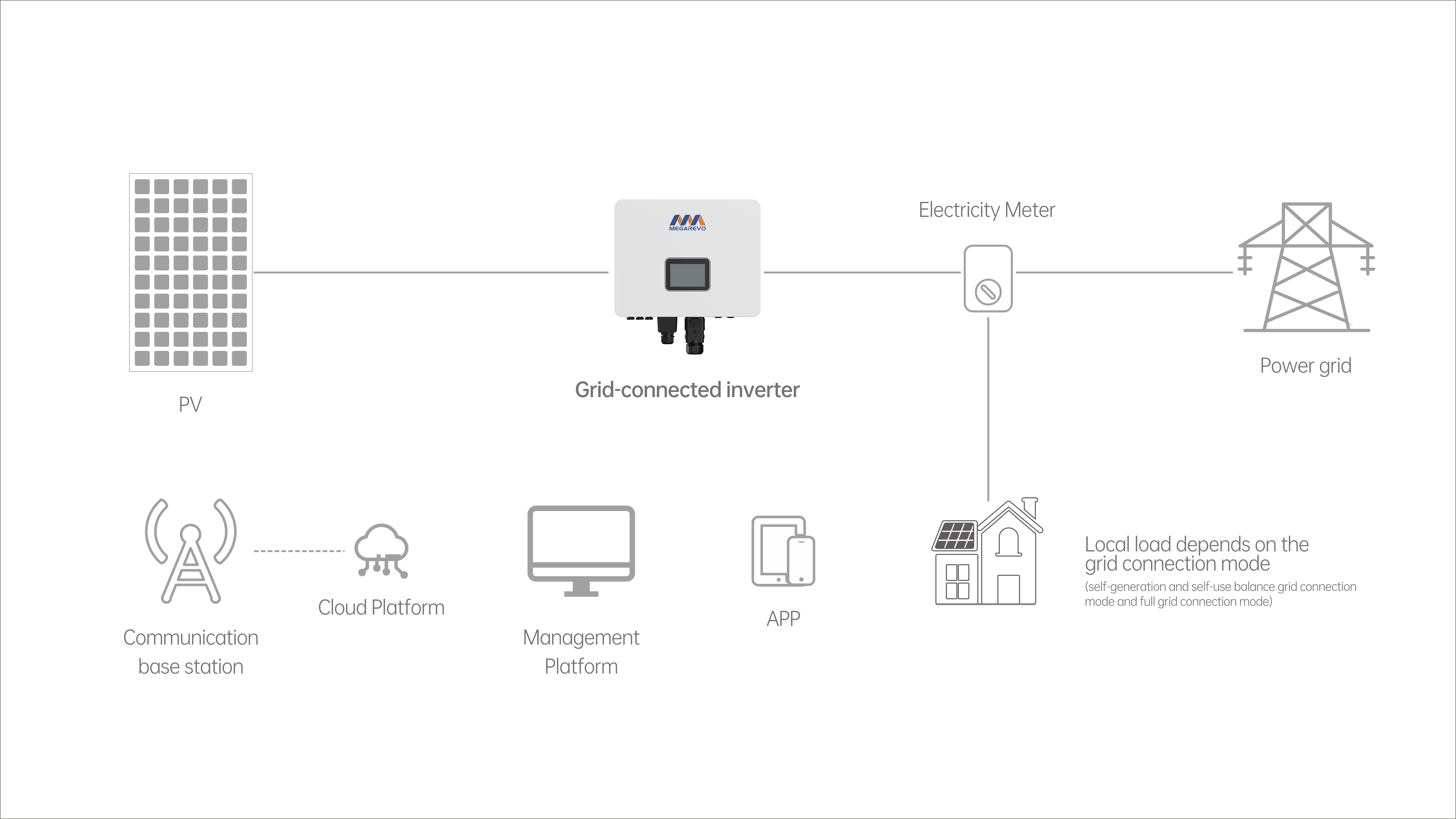
Hybrid Inverter
Hybrid inverters integrate the functions of both off-grid and on-grid inverters, operating independently in solar power systems or being integrated into large-scale power grids. They can be flexibly switched between operating modes according to the actual requirements, thereby achieving optimal energy efficiency and performance.
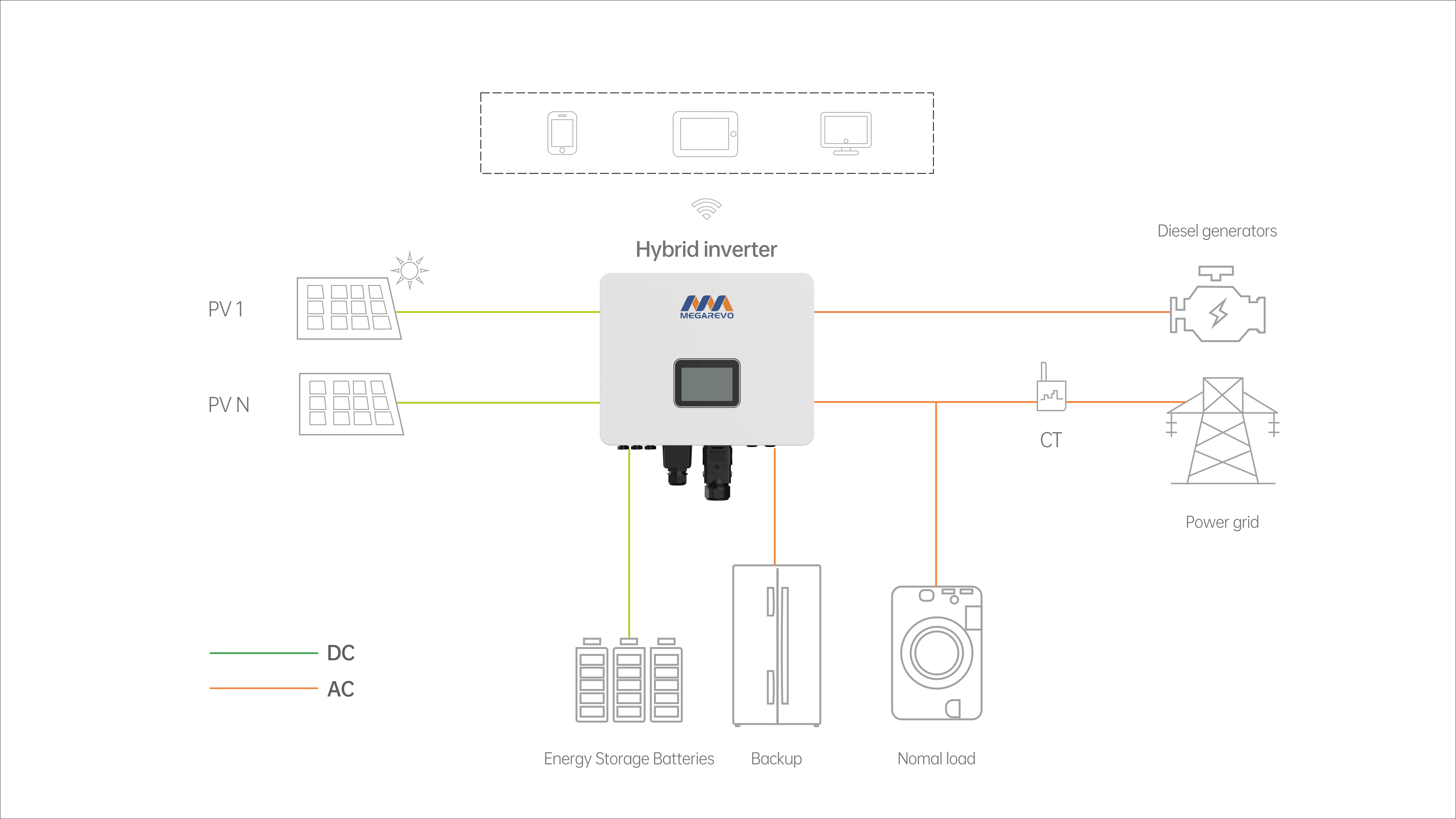
Inverter Advantages and Challenges
Off-grid inverters
Advantages:
1. Independent operation capability: an independent system that does not rely on the power grid. Regardless of whether there is utility power, as long as there is sunlight to meet, the off-grid system can work independently, you can independently provide electricity.
2. Flexible installation and deployment
Challenges:
1. Higher costs: The initial investment cost for off-grid systems is relatively high, as they require the installation of battery systems and other equipment.
2. Strong dependence on location: They can only work intermittently, and the power generation is affected by cloudy, rainy, snowy, and hazy weather conditions.
On-grid inverters
Advantages:
1.Economic efficiency: Without the need for expensive batteries, the system's purchase cost and maintenance expenses are relatively low.
2. Quick return on investment: The typical payback period for the system is 4 to 6 years.
3.Synchronization with the grid: on-grid inverters are able to operate in synchronization with the grid, ensuring that the power output is in line with the grid standard, making them suitable for large-scale grid-connected applications.
Challenges:
1. Sensitivity to grid fluctuations: any fluctuation in the grid may affect the performance of on-grid inverter due to the need to synchronize with the grid.
2. Weak islanding protection: may not be able to disconnect in time in case of grid failure.
Hybrid Inverter
Advantages:
1. Flexibility: Hybrid inverters can be switched between off-grid and on-grid modes as required, providing maximum flexibility and energy efficiency.
2. Energy Management: The integrated management of solar energy and battery storage optimizes energy usage and reduces electricity costs.
Challenges:
1. Islanding protection: Hybrid inverters are not as tightly protected against islanding as off-grid inverters and may not provide adequate protection in the event of a grid fault.
2. Higher upfront initial investment costs
Conclusion
Different inverters possess distinct functionalities and applications, necessitating that end consumers understand their specific requirements before making a purchase. They should consult with professional manufacturers or installers to clarify these needs and subsequently develop a comprehensive energy solution plan.